In industrial and infrastructure projects, structural reliability depends not only on material strength but also on consistency, predictability, and long-term durability. As composite materials become more widely adopted, standard composite structural profiles play an increasingly important role in ensuring stable performance across different applications and environments. These standardized FRP profiles support engineering accuracy, reduce design uncertainty, and improve lifecycle performance compared with non-standard or customized structural components.
Through its STRONX pultruded product line, THE FRONT manufactures FRP structural profiles designed to meet industrial expectations for consistency, durability, and repeatable quality, supporting both domestic and international projects.
What Are Standard Composite Structural Profiles?
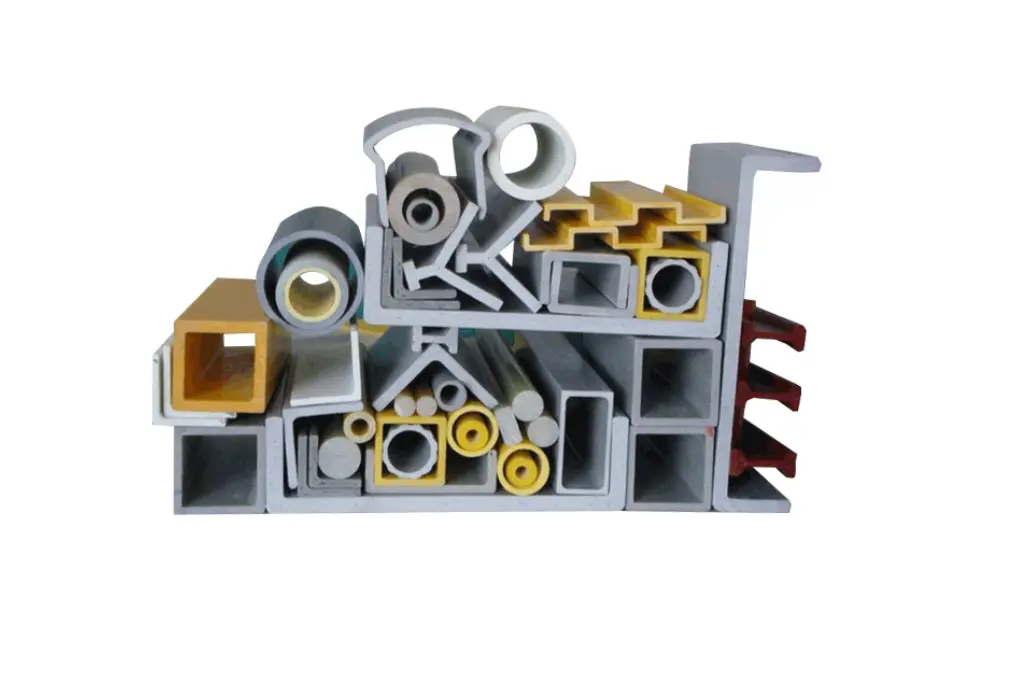
Standard composite structural profiles are pultruded FRP sections manufactured with defined geometry, consistent dimensions, and predictable material behavior.
Unlike custom-fabricated components, standard profiles are designed around repeatable cross-sections such as beams, channels, angles, and tubes. This standardization allows engineers to specify structural elements with confidence, knowing that mechanical properties and dimensional tolerances remain stable across production batches.
For industrial structures, this consistency is critical. It simplifies structural calculations, supports modular design, and reduces variability during installation and operation.
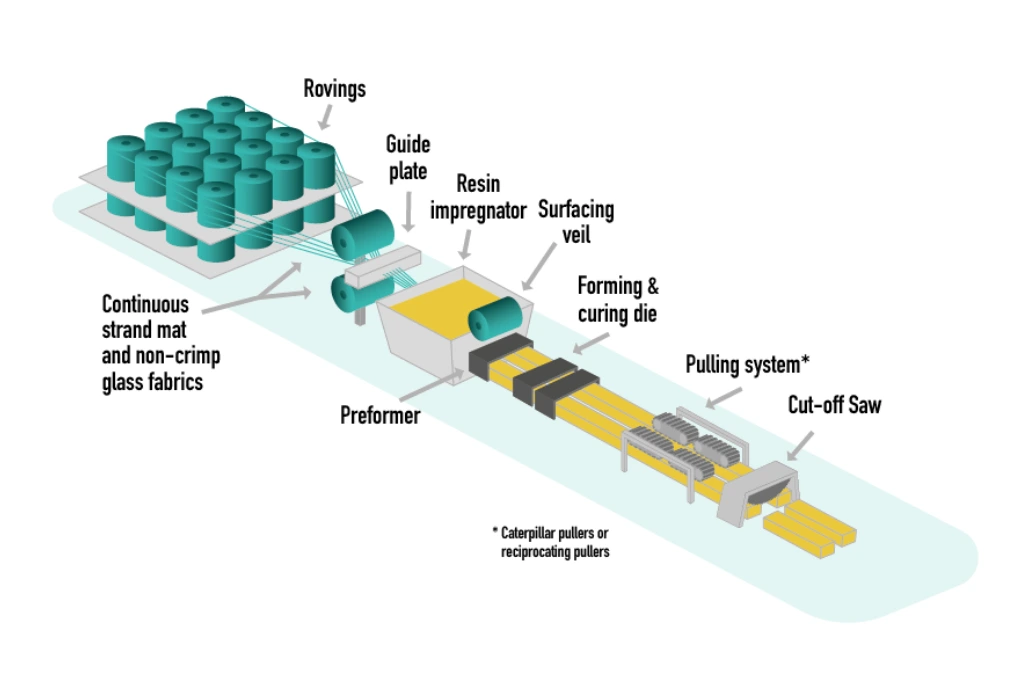
Structural Consistency Through Controlled Manufacturing
Structural consistency begins with a controlled production process.
Pultruded FRP structural profiles are produced using continuous fiber reinforcement and stable resin systems. Because fibers are aligned along the length of the profile, load paths remain predictable, and mechanical performance is consistent throughout the component.
Standard composite profiles benefit from:
- Uniform fiber distribution
- Stable wall thickness
- Constant cross-section along the entire length
- Repeatable mechanical properties
These characteristics reduce the risk of weak points or dimensional deviation, which are common challenges in non-standard or batch-based fabrication.
Durability as a Core Performance Advantage
Durability is one of the primary reasons standard composite structural profiles are selected for industrial environments.
FRP structural profiles resist corrosion, moisture, and many chemical agents that degrade steel or aluminum over time. This inherent resistance allows composite structures to maintain performance in aggressive environments such as chemical plants, wastewater facilities, coastal installations, and industrial roofs.
Because FRP does not rust or require protective coatings, standard composite profiles offer longer service life with lower maintenance demands, directly improving lifecycle cost efficiency.
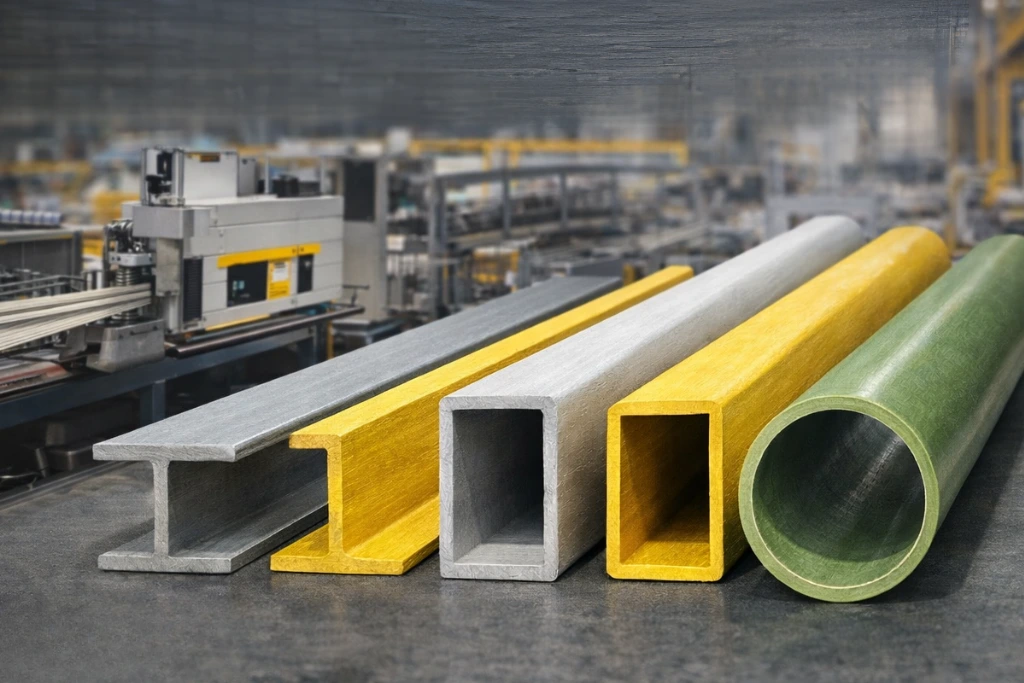

Role of Standardization in Engineering Design
Standardization improves design accuracy and reduces engineering risk.
When engineers work with standard composite structural sections, they can rely on known geometries and performance ranges. This simplifies load calculations, connection detailing, and system integration. It also improves compatibility between different structural components within the same project.
Standard profiles support:
- Faster design cycles
- Easier comparison between material options
- Improved coordination between designers, manufacturers, and contractors
- Reduced on-site adjustments during installation
These advantages are particularly valuable in large-scale industrial and infrastructure projects.
Industry References: EN 13706 and ASTM D638
In global composite engineering discussions, EN 13706 and ASTM D638 are commonly referenced as industry benchmarks.
EN 13706 European standards are often cited as a classification framework for pultruded FRP structural profiles. They help describe profile categories, typical applications, and general performance expectations, supporting clearer communication across European and international markets.
ASTM D638, on the other hand, is widely referenced in relation to tensile properties of plastic and composite materials. While not specific to structural profile design, it provides insight into material behavior under tensile loading, which is relevant when evaluating FRP structural performance.
These standards are used in the industry as reference points to support material understanding and comparison, rather than as direct claims tied to any single manufacturer.
Performance Features of FRP Structural Profiles
Standard composite structural profiles deliver a balanced combination of mechanical and functional performance.
Key performance features include:
- High strength-to-weight ratio, reducing overall structural load
- Dimensional stability, supporting accurate assembly
- Electrical non-conductivity, suitable for electrical and industrial facilities
- Thermal stability, reducing deformation under temperature variation
- Resistance to corrosion and moisture, ensuring long-term durability
These features allow FRP structural profiles to perform reliably in environments where traditional materials struggle to maintain performance over time.
Technical Characteristics That Support Long-Term Use
Technical characteristics play a critical role in the long-term performance of standard composite profiles.
Pultruded FRP structural sections typically feature:
- Continuous fiber reinforcement for axial strength
- Consistent resin impregnation for environmental protection
- Controlled curing to minimize internal stress
- Stable surface quality suitable for outdoor exposure
These characteristics help maintain mechanical performance and structural integrity throughout the service life of the profile.
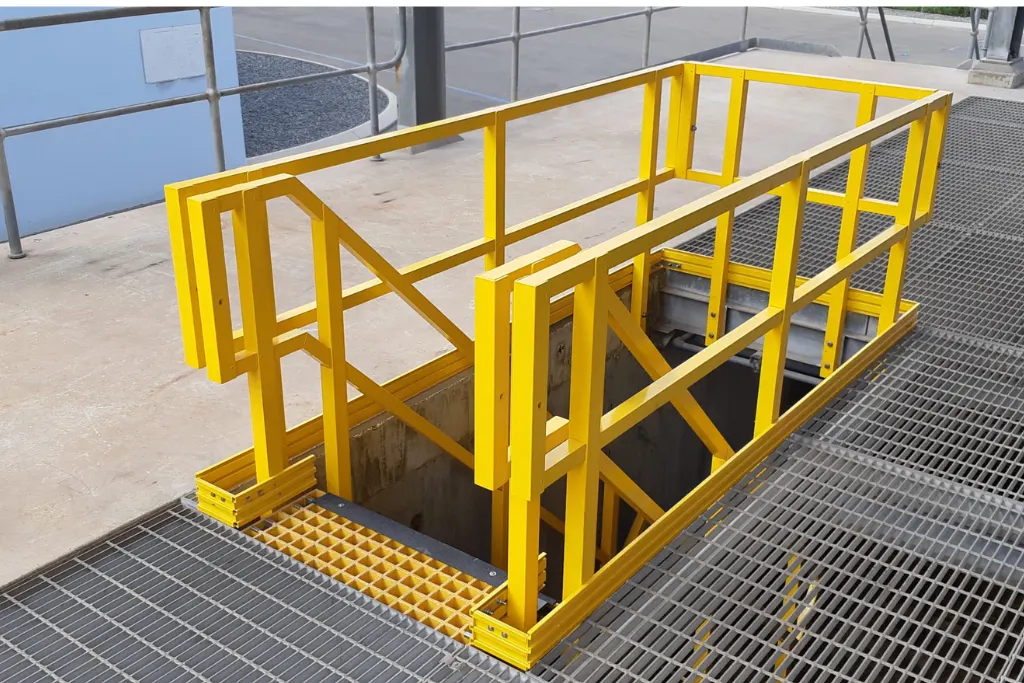
Applications Where Consistency and Durability Matter Most
Standard composite structural profiles are widely used in applications where performance reliability is critical.
Common applications include:
- Industrial roof structures and purlin systems
- Structural frames for factories and warehouses
- Walkways, platforms, and support structures
- Chemical and wastewater treatment facilities
- Infrastructure exposed to moisture and corrosive agents
In these environments, structural consistency reduces maintenance risk, while durability ensures long-term operational stability.
THE FRONT and the STRONX Pultruded Profile Line
THE FRONT manufactures standard composite structural profiles through its STRONX pultruded product line.
STRONX profiles are designed for industrial use, offering consistent geometry and stable mechanical performance. The product range includes various FRP structural shapes suitable for load-bearing frames, roofing systems, and support structures.
By focusing on controlled production and material reliability, THE FRONT supports customers seeking dependable composite solutions for demanding industrial applications.
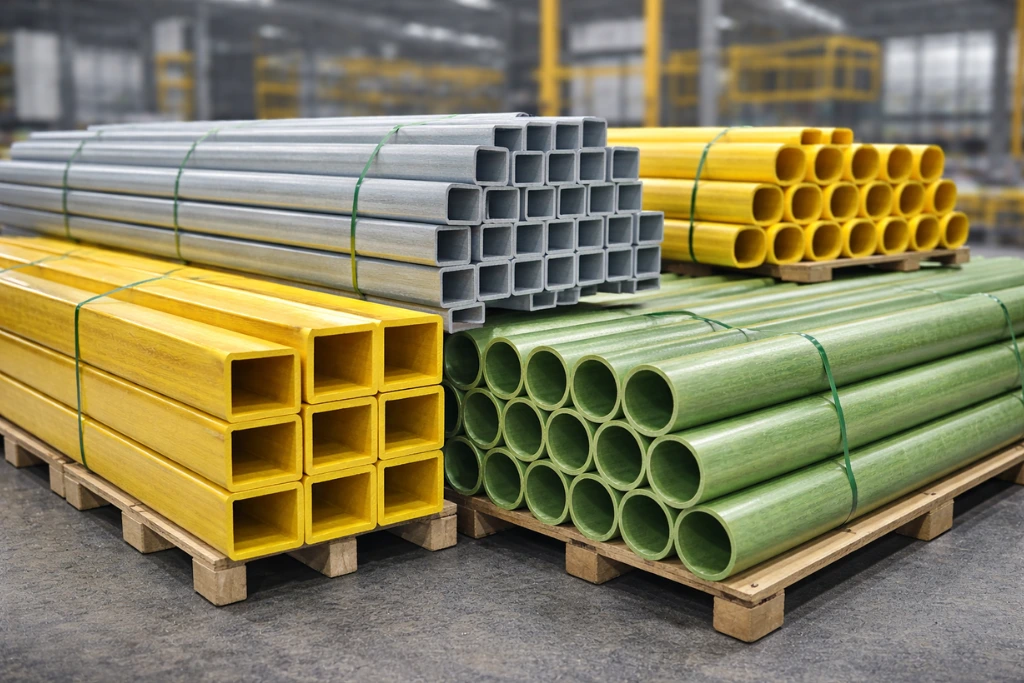
Manufacturing Stability and Export-Oriented Supply
Manufacturing stability is essential for supplying standard composite structural profiles to global markets.
THE FRONT operates pultrusion lines capable of continuous production with uniform quality, supporting large-volume orders and repeat supply. Export-oriented handling and logistics ensure that FRP profiles arrive at overseas project sites in suitable condition for installation.
This combination of manufacturing consistency and export readiness allows THE FRONT to support international projects requiring reliable composite structural components.
Standard composite structural profiles play a vital role in improving structural consistency and durability in modern engineering.
Through controlled pultrusion manufacturing, standardized FRP structural profiles provide predictable performance, environmental resistance, and long service life across industrial applications.
By supplying pultruded profiles through its STRONX product line, THE FRONT supports projects that prioritize reliability, durability, and long-term value. As industries continue to adopt composite materials, standard composite structural profiles will remain essential elements in building stable and resilient structures.





