In modern industrial engineering, load-bearing frames are expected to deliver more than just structural strength. They must remain stable under continuous loads, resist harsh environmental conditions, and minimize long-term maintenance. Traditional materials such as steel or concrete have long dominated this role, but increasing exposure to corrosion, weight constraints, and lifecycle cost pressures are driving engineers to reconsider material choices.
FRP structural profiles for load-bearing frames are increasingly specified in industrial projects where durability, lightweight performance, and structural reliability are critical. Manufactured through pultrusion, these composite profiles provide a balanced combination of strength, consistency, and environmental resistance.
Load-Bearing Frames in Industrial Engineering
Load-bearing frames form the structural backbone of industrial facilities.
They support roofs, platforms, equipment, walkways, and secondary structures, transferring loads safely to foundations. In industrial environments, these frames are exposed to static loads, dynamic forces, vibration, temperature variation, and often corrosive conditions.
The performance of load-bearing frames directly affects:
- Structural safety
- Operational continuity
- Maintenance frequency
- Total lifecycle cost
As a result, material selection for these frames is a critical engineering decision.

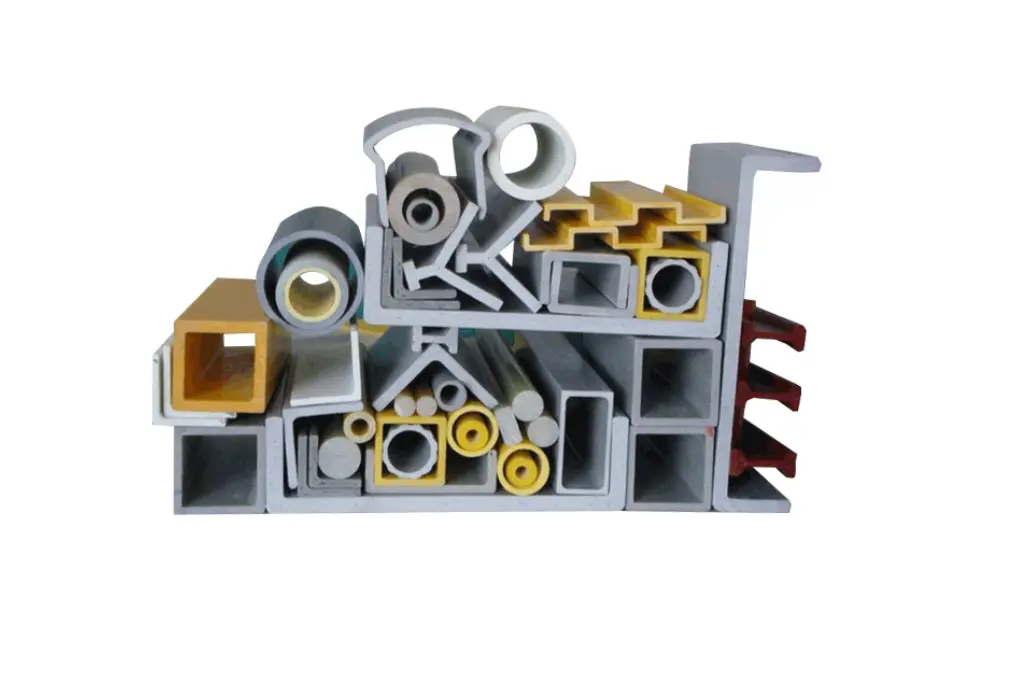
What Are FRP Structural Profiles?
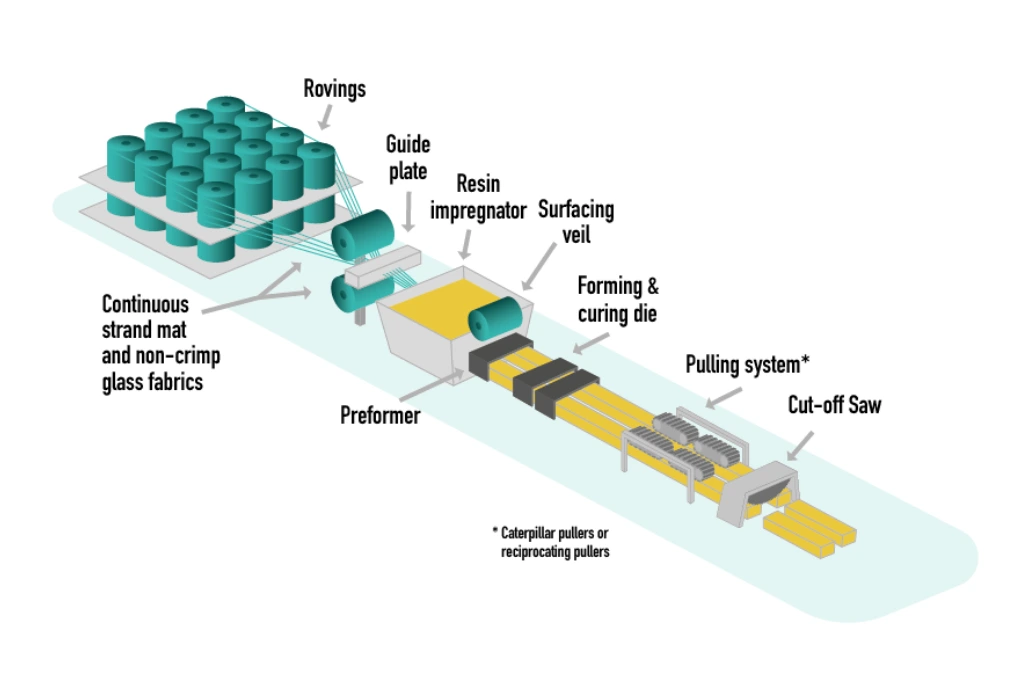
FRP structural profiles are composite sections manufactured using a continuous pultrusion process.
They are reinforced with continuous fiberglass fibers embedded in a thermoset resin matrix. This process produces profiles with uniform cross-sections and predictable mechanical properties along their entire length.
Common FRP structural shapes used in load-bearing frames include:
- FRP beam and FRP I-beam profiles
- FRP C channels and angles
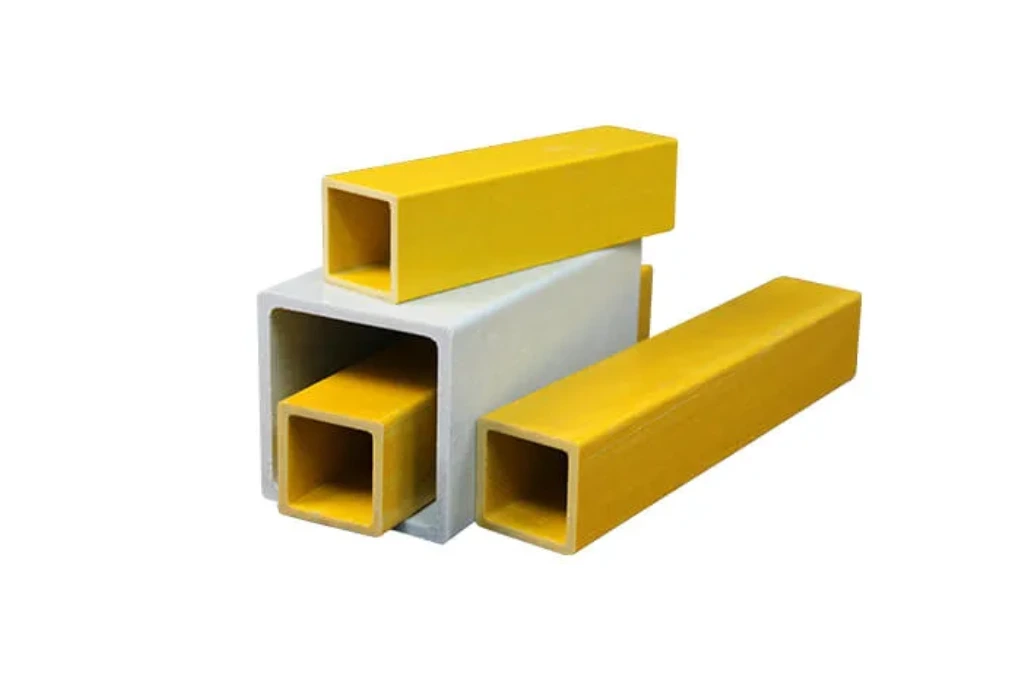
- Square and rectangular FRP tubes
- Round FRP tubes
These standardized profiles allow engineers to design complete structural frames using consistent composite components.
Structural Strength and Load-Bearing Capability
Pultruded FRP structural profiles are engineered to carry significant loads efficiently.
Continuous fiber reinforcement is aligned along the length of the profile, allowing loads to be transferred directly through the fibers. This results in high axial strength and stable performance under bending and compression when profiles are properly selected and designed.
While FRP has a lower elastic modulus than steel, section geometry and profile depth are used to achieve required stiffness. In many industrial applications, this trade-off is offset by the material’s durability and reduced structural weight.
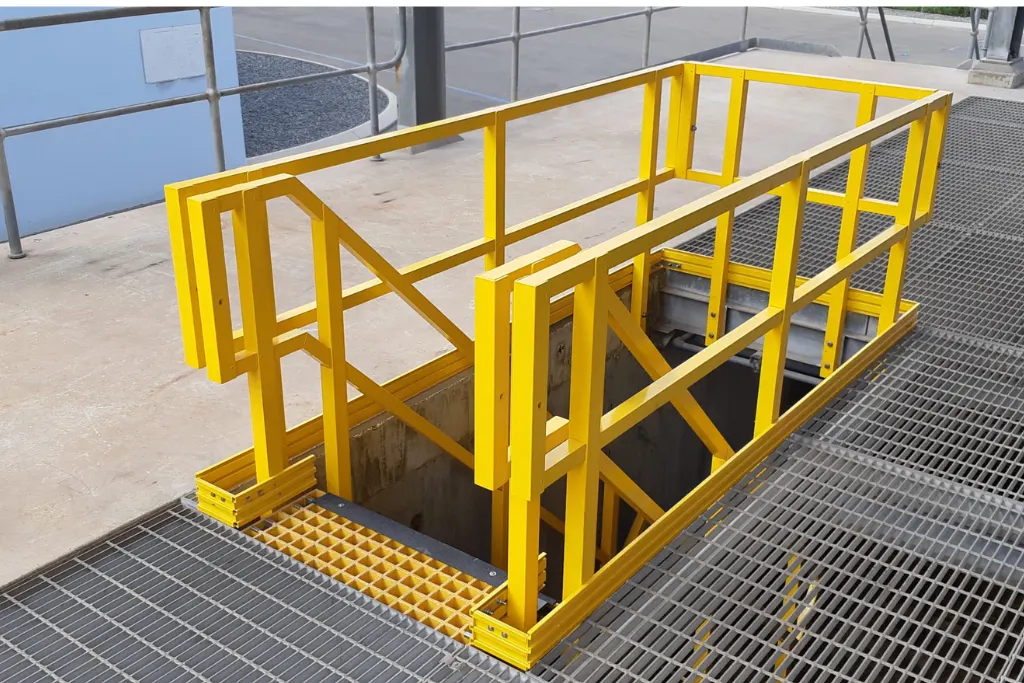

Lightweight Advantage in Structural Design
One of the most important advantages of FRP structural profiles is their lightweight nature.
Lightweight fiberglass profiles significantly reduce dead load compared to steel structures. This provides several engineering benefits:
- Easier handling and installation
- Reduced foundation loads
- Simplified transportation and logistics
- Lower installation time and labor cost
For large-span structures and elevated frames, lightweight high-strength FRP beams help optimize overall structural efficiency.
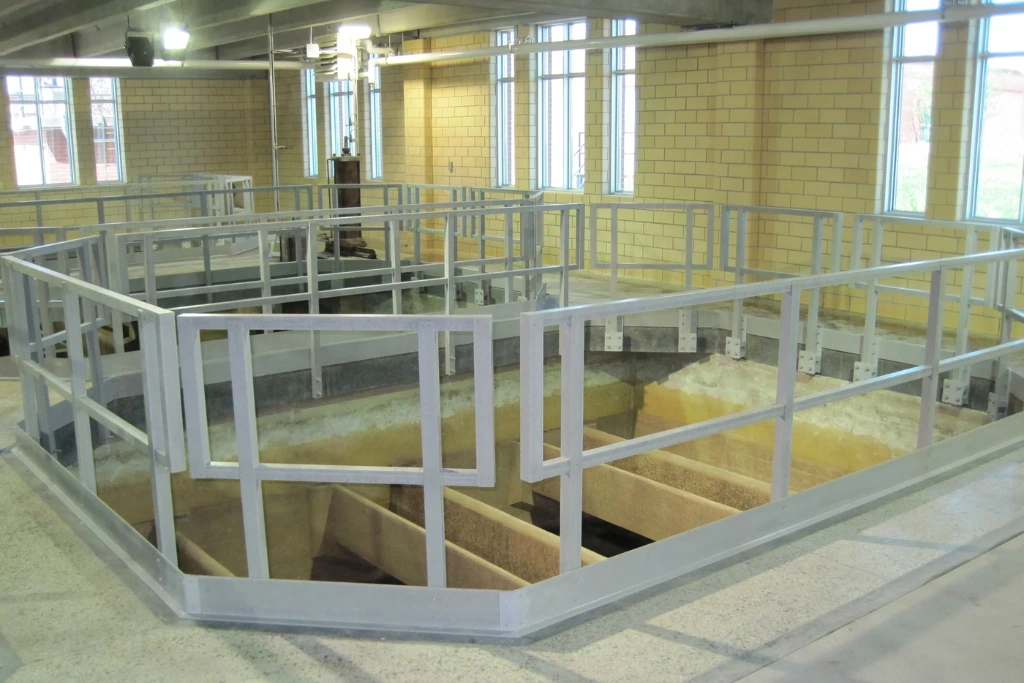
Durability in Corrosive Industrial Environments
Durability is a key reason FRP profiles are selected for load-bearing frames.
Unlike steel, which relies on coatings or galvanization for protection, FRP profiles are inherently corrosion resistant throughout their entire cross-section. Exposure to moisture, chemicals, salt air, or industrial fumes does not lead to rust or material degradation.
This makes FRP structural profiles particularly suitable for:
- Chemical processing plants
- Wastewater treatment facilities
- Coastal and marine-related infrastructure
- Industrial warehouses with high humidity
By maintaining structural integrity over time, FRP frames reduce the need for frequent inspection and repair.
Applications of FRP Structural Profiles in Load-Bearing Frames
FRP structural profiles are widely used in industrial load-bearing applications.
Typical applications include:
- Structural frames for factories and processing plants
- FRP warehouse structures requiring long-span supports
- Industrial roof frames exposed to aggressive environments
- Support structures for equipment and piping systems
- Platforms, walkways, and access structures
In these applications, FRP beams and columns provide reliable load-bearing performance while minimizing maintenance demands.
Predictability and Design Consistency
Design consistency is essential in load-bearing structural systems.
Pultruded FRP profiles offer uniform geometry and repeatable material properties, allowing engineers to perform structural calculations with confidence. This predictability supports modular construction, prefabrication, and standardized frame designs.
For industrial engineering projects, consistent FRP structural profiles reduce design uncertainty and simplify coordination between designers, manufacturers, and contractors.
Safety and Functional Benefits
Beyond strength and durability, FRP structural profiles offer additional safety benefits.
FRP is electrically non-conductive, reducing risk in facilities with electrical equipment or power distribution systems. It also exhibits lower thermal conductivity than metal, helping reduce thermal bridging in structural frames.
These properties make FRP structural frames suitable for industrial environments where safety and operational reliability are priorities.
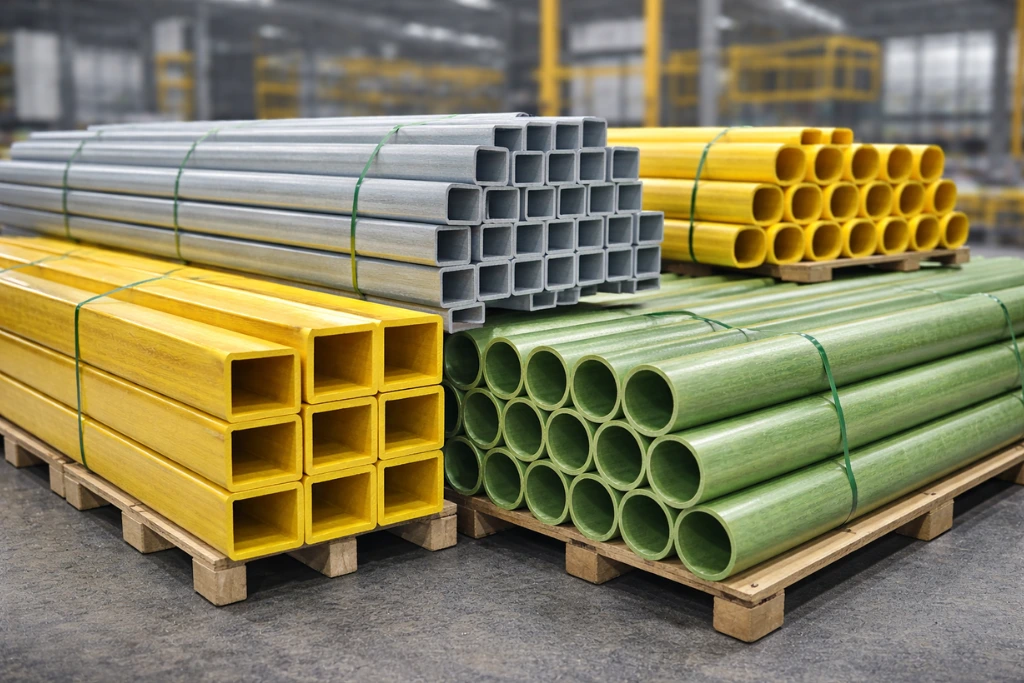
THE FRONT and STRONX Pultruded Structural Profiles
THE FRONT manufactures FRP structural profiles for load-bearing frames through its STRONX product line.
STRONX, the pultruded composite line of THE FRONT, includes FRP beams, I-beam profiles, channels, angles, and tubular sections designed for industrial structural applications. The product line supports projects requiring lightweight, high-strength, and corrosion-resistant structural components.
THE FRONT focuses on controlled manufacturing processes and export-oriented supply, enabling its FRP profiles to be used in both domestic and international industrial projects.
Long-Term Engineering Value
The long-term engineering value of FRP structural profiles lies in lifecycle performance.
By reducing corrosion-related maintenance, repainting, and structural replacement, FRP frames lower total cost of ownership. For facilities designed to operate continuously under harsh conditions, this reliability provides clear operational and financial advantages.
As industrial engineering continues to evolve toward durable and sustainable solutions, FRP structural profiles are becoming an increasingly strategic material choice for load-bearing frames.
FRP structural profiles for load-bearing frames provide a reliable and durable solution for modern industrial engineering.
By combining lightweight performance, high strength, corrosion resistance, and predictable structural behavior, pultruded FRP profiles address many limitations of traditional materials.
Through its STRONX product line, THE FRONT supports industrial projects with FRP structural profiles designed for long-term load-bearing performance. As industrial environments become more demanding, FRP structural frames continue to demonstrate strong engineering value in both performance and durability.