FRP panels combine fiberglass strength with plastic flexibility, making them lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and highly durable. Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic (FRP) panels are an innovative composite material that blends the strength of fiberglass with the flexibility and resilience of plastic. This unique composition results in lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and highly durable panels that outperform traditional materials in various applications. From construction and industrial facilities to transportation and marine environments, FRP panels are engineered for longevity and reliability. This article delves into the science behind FRP panels, detailing their manufacturing process and explaining why they last longer than conventional alternatives.

What Are FRP Panels?
- Composite structure: Polymer plastic resin reinforced with fiberglass for strength and durability.
- Key properties: Moisture-proof, fire-retardant, impact-resistant, and chemically resistant. FRP panels are composite sheets composed of a polymer plastic resin reinforced with fine glass fibers. The fiberglass reinforcement provides excellent tensile strength, while the plastic matrix creates a smooth, non-porous, and chemically resistant surface. This combination results in lightweight, impact-resistant panels, moisture-proof, fire-retardant, and exceptionally durable. These properties make FRP panels a preferred material for industries requiring high-performance building solutions.
How Are FRP Panels Manufactured?
- Material selection: Thermosetting polymers and high-strength fiberglass.
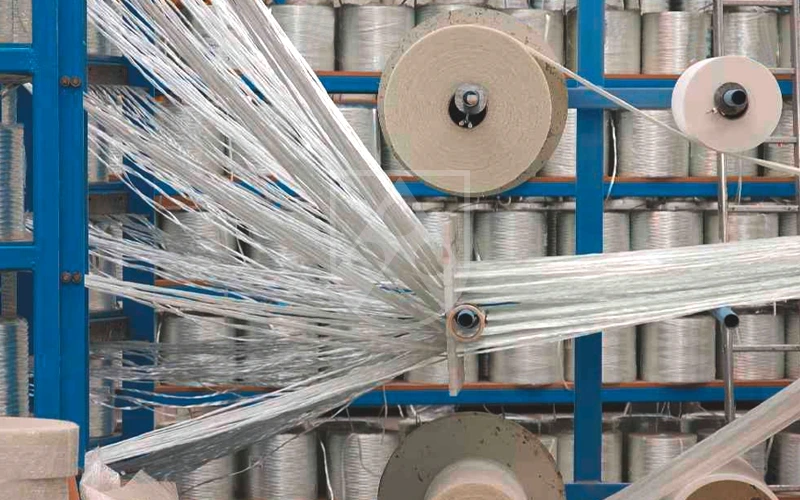
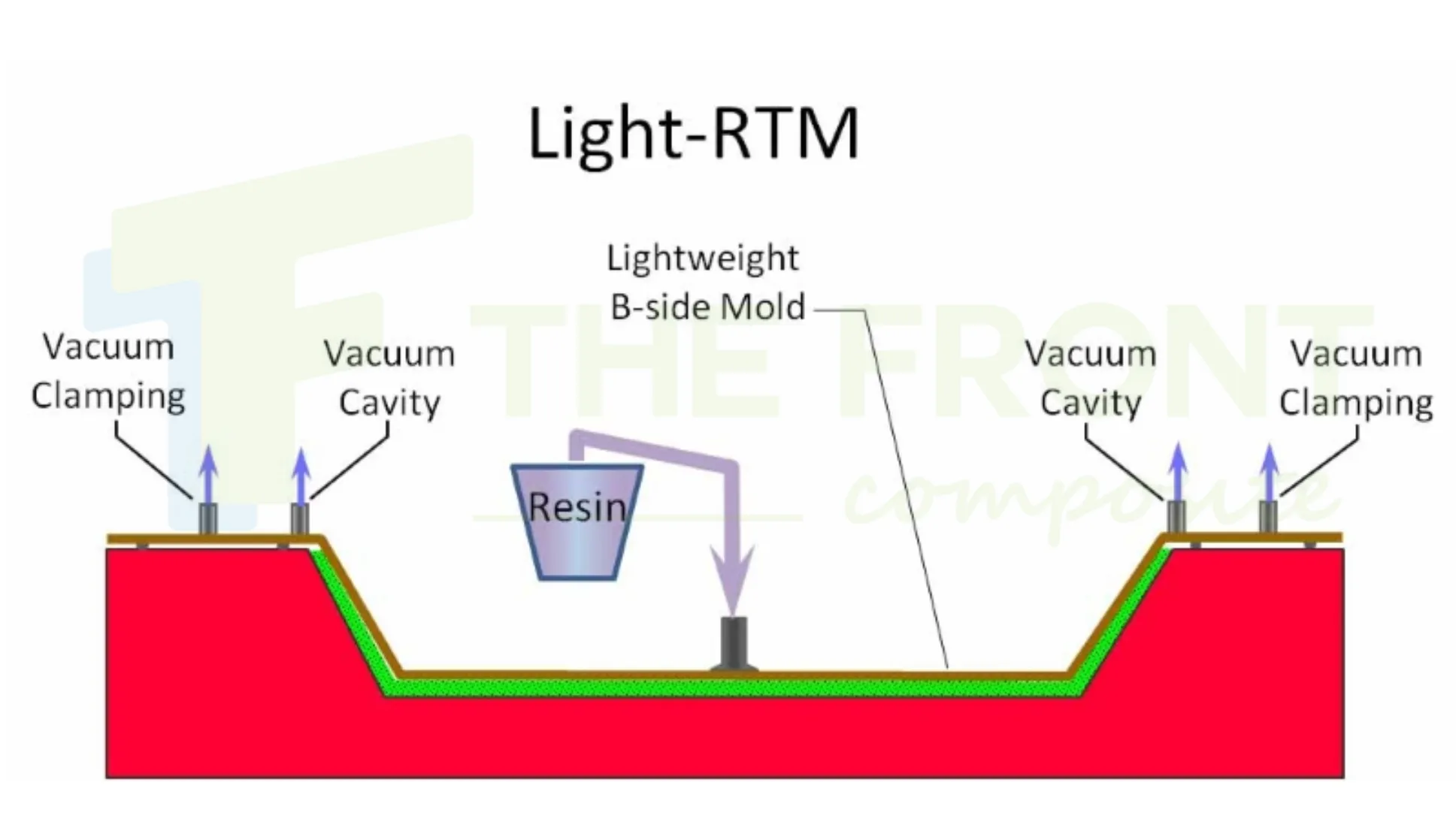
- Manufacturing steps: Impregnation with resin, polymerization with heat/pressure, and protective gel coat application. The manufacturing of FRP panels is a highly specialized process designed to ensure uniform strength, consistency, and longevity. The first step in the process involves material selection, where a thermosetting polymer is chosen as the binding agent. This resin provides resistance to chemicals, UV exposure, and moisture, ensuring the longevity of the panels. High-strength woven glass fibers, chopped strand mats, or continuous rovings are embedded within the resin to reinforce structural integrity.
Once the materials are prepared, the fiberglass reinforcement is placed onto a mold or a continuous conveyor system. The resin mixture is applied to fully saturate the fiberglass through a process called impregnation, ensuring a uniform and well-bonded composite structure. The impregnated material then undergoes a polymerization process, where heat and pressure are applied to trigger a chemical reaction that solidifies and strengthens the panel. This controlled curing process eliminates voids and imperfections, enhancing the panel’s durability and resistance to external stressors.
After curing, FRP panels receive a protective gel coat that serves as a barrier against environmental damage. This coating prevents surface degradation from UV radiation, chemicals, and abrasions while also improving impact resistance. Additionally, this stage allows for the customization of FRP panels with smooth or textured surfaces tailored to specific applications. Finally, the panels are precision-cut into standardized or custom dimensions to meet industry requirements, with additional features such as fire-retardant layers, anti-slip surfaces, and reinforced edges incorporated for specialized needs.
Why Do FRP Panels Last Longer Than Traditional Materials?
- High strength-to-weight ratio: Stronger than aluminum and steel per weight.
- Corrosion and chemical resistance: Ideal for harsh environments like labs, marine settings, and industrial sites.
- Low maintenance: No frequent repainting or sealing needed. The longevity of FRP panels is attributed to their engineered composition, which provides multiple performance advantages over traditional materials such as wood, metal, and conventional plastics. One of the primary reasons FRP panels outlast other materials is their high strength-to-weight ratio. They are significantly stronger than aluminum and steel on a per-weight basis, making them ideal for applications where weight reduction enhances efficiency, such as in aerospace, automotive, and modular construction.
Unlike metal panels that rust or wood that decays, FRP panels are highly resistant to environmental factors. Their resistance to acids, alkalis, and industrial chemicals makes them well-suited for harsh conditions, including laboratories, clean rooms, and marine structures. Additionally, FRP panels can withstand high-impact forces without cracking or breaking, making them a durable choice for industrial environments and high-traffic areas. Their non-porous surface also prevents bacterial growth, making them an excellent solution for food processing and healthcare settings.

Maintenance requirements for FRP panels are minimal compared to traditional materials. Unlike wood, which requires regular sealing, or metal, which needs painting and rust protection, FRP panels are inherently low-maintenance. They do not require frequent repainting or chemical treatments, and they outlast materials like metal and wood in extreme weather conditions. Many FRP panels are also designed with fire-retardant properties, ensuring compliance with stringent building safety codes. Additionally, UV-resistant coatings prevent fading, brittleness, and structural degradation caused by prolonged sun exposure.
Applications of FRP Panels
- Construction: Used for roofing, walls, ceilings, and flooring.
- Transportation & Automotive: Applied in truck bodies, railcar interiors, and lightweight vehicle components.
- Marine & Offshore: Perfect for ship decks, boat hulls, and saltwater environments.
- Healthcare & Cleanrooms: Provides sterile, chemical-resistant surfaces for safe environments. The superior durability and versatility of FRP panels make them widely applicable across multiple industries. In the construction sector, FRP panels are commonly used for roofing, wall panels, ceilings, and flooring, providing moisture and impact resistance. In the transportation and automotive industries, FRP panels are utilized in truck bodies, railcar interiors, and lightweight vehicle components to enhance structural performance.

In marine and offshore industries, FRP panels serve as essential materials for boat hulls, ship decks, and docks, offering superior resistance to saltwater corrosion. They are also widely used in food processing facilities and cleanroom environments, where non-porous, easy-to-clean surfaces are essential. Additionally, FRP panels are a key component in healthcare and laboratory settings, where their chemical-resistant properties contribute to a sterile and safe environment.
Why Choose FRP Panels?
- Future-proof building material: Offers unparalleled durability, safety, and environmental resistance.
- Cost-effective investment: Low maintenance and long-lasting compared to traditional materials. FRP panels represent the future of high-performance building materials, offering unparalleled durability, safety, and environmental resistance compared to conventional alternatives. Their longevity and low maintenance requirements make them a cost-effective investment for industries that demand reliable, high-strength materials. Whether for construction, transportation, marine applications, or specialized industrial use, FRP panels provide a superior combination of performance, efficiency, and sustainability.
The Front is a trusted leader in FRP panel solutions, offering durable and high-performance materials for various industries. Our advanced manufacturing ensures top-quality FRP panels that meet industry standards. Contact us today to explore our customizable FRP solutions for your project.