Industrial facilities operating in corrosive environments face persistent challenges related to structural degradation, maintenance downtime, and safety risks. Traditional structural materials such as carbon steel or coated metal frames often deteriorate rapidly when exposed to moisture, chemicals, salt air, or industrial fumes. As a result, engineers and project owners are increasingly evaluating alternative structural systems that can deliver long-term durability with lower maintenance demands.
FRP structural frames, built from pultruded composite profiles, have emerged as a practical solution for these conditions. Their inherent resistance to corrosion, combined with structural reliability, makes them well suited for industrial environments where durability is critical.
Understanding Corrosive Industrial Environments
Corrosive environments are defined by continuous exposure to elements that accelerate material degradation.
Common examples include chemical processing plants, wastewater treatment facilities, coastal warehouses, fertilizer factories, and food processing plants. In these settings, steel structures are exposed to moisture, acidic vapors, salts, and aggressive cleaning agents. Even with protective coatings, corrosion often begins at joints, fasteners, and damaged surfaces.
Over time, corrosion leads to section loss, reduced load-bearing capacity, and increased inspection and repair costs. This has driven interest in structural materials that are inherently resistant rather than reliant on surface protection.
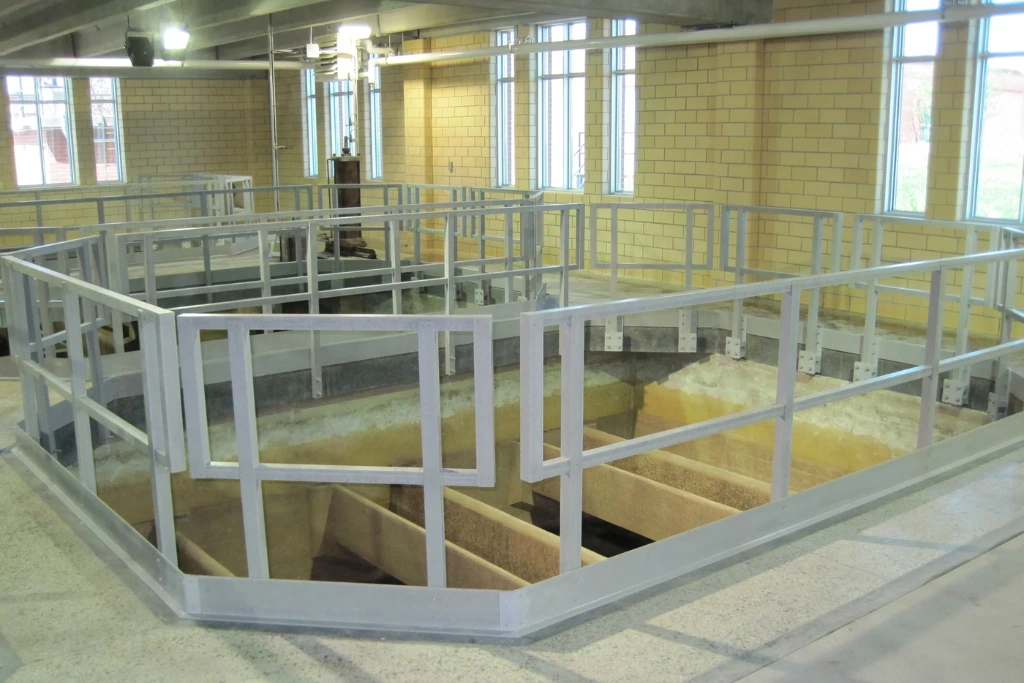

What Are FRP Structural Frames?
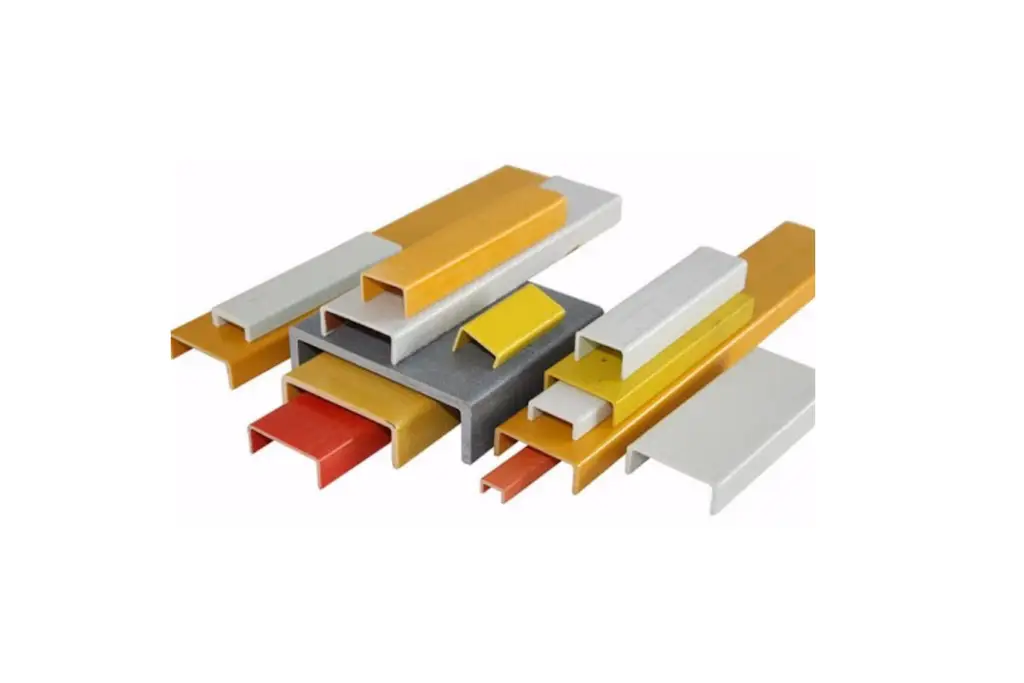
FRP structural frames are load-bearing systems assembled from pultruded FRP structural profiles.
These frames typically use standardized FRP structural shapes such as:
- Pultruded FRP I beams
- FRP C channels
- FRP angles
- Square and rectangular FRP tubes
- Round FRP tubes
The profiles are manufactured using a pultrusion process that aligns continuous glass fibers along the length of the profile, creating consistent mechanical properties and predictable structural behavior.
Because FRP does not rust or oxidize, structural frames made from these profiles maintain their integrity even in aggressive industrial environments.
Why FRP Structural Frames Perform Better in Corrosive Conditions
The durability of FRP structural frames comes from material composition, not surface treatment.
Unlike steel, which depends on coatings or galvanization for protection, FRP profiles are corrosion resistant throughout their entire cross-section. Exposure to moisture, chemicals, or industrial fumes does not compromise the structural core.
Key durability advantages include:
- Resistance to chemical corrosion and moisture
- No rusting or flaking over time
- Stable performance in humid or coastal environments
- Reduced risk of hidden internal degradation
These characteristics make FRP structural frames particularly suitable for facilities where corrosion-related maintenance is costly or disruptive.
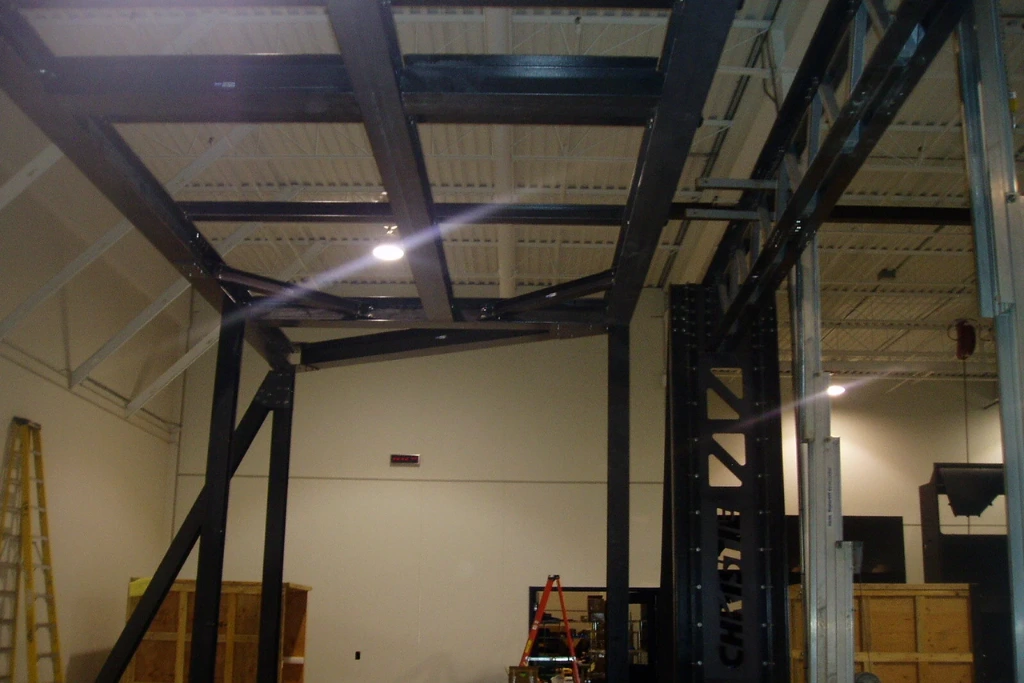

Application: FRP Structural Frames in Industrial Roof Systems
One of the most common applications of FRP structural frames is in industrial roof structures.
FRP industrial roof frames often consist of FRP beams, columns, and purlins supporting roofing panels. In corrosive environments, steel roof frames frequently require repainting, replacement of corroded sections, or reinforcement after only a few years of service.
By contrast, FRP roof frames maintain structural performance without protective coatings. Their lightweight nature also reduces load on primary supports and foundations, simplifying overall structural design.
This makes FRP roof frames particularly effective for factories and warehouses exposed to humidity, chemical vapors, or saline air.
Application: FRP Warehouse Structures in Aggressive Environments
Warehouses used for chemicals, raw materials, or processed goods often experience elevated corrosion risk.
FRP warehouse structures benefit from:
- Lightweight FRP beams and columns that simplify installation
- Corrosion resistance that protects long-term structural integrity
- Dimensional stability under varying temperature and humidity conditions
In facilities with high ceilings or large spans, FRP structural frames reduce the need for frequent inspection and maintenance, improving operational continuity.
Case Study Simulation: Chemical Processing Facility
Consider a simulated chemical processing plant operating in a high-humidity, corrosive environment.
The facility requires elevated walkways, equipment support structures, and roof frames exposed to chemical vapors. A conventional steel frame system would require regular coating inspection and periodic replacement of corroded components.
Using FRP structural frames assembled from pultruded FRP beams and columns, the facility benefits from:
- Consistent structural performance without corrosion-related degradation
- Reduced maintenance scheduling and downtime
- Improved safety due to electrical non-conductivity
- Longer service intervals compared to steel structures
This simulation reflects common outcomes observed in industrial applications where FRP replaces traditional materials.
Structural Performance and Load-Bearing Capability
FRP structural frames can meet load-bearing requirements when properly designed.
Pultruded FRP profiles align fibers in the primary load direction, providing efficient load transfer and predictable mechanical behavior. While FRP has a lower elastic modulus than steel, section geometry and profile selection compensate for this difference in many industrial applications.
FRP beams and columns are commonly used in:
- Support structures
- Equipment frames
- Roof and platform systems
- Industrial frameworks
Engineering design focuses on optimizing profile geometry to achieve required stiffness and strength while maintaining lightweight benefits.
Additional Performance Benefits in Industrial Settings
Beyond corrosion resistance, FRP structural frames offer functional advantages.
FRP is electrically non-conductive, reducing risk in facilities with electrical equipment or overhead power systems. It also exhibits low thermal conductivity compared to metals, helping reduce thermal bridging in roof and wall structures.
These properties improve overall safety and energy performance in industrial buildings.
THE FRONT and the STRONX FRP Structural Frame System
THE FRONT manufactures FRP structural frames using pultruded profiles through its STRONX product line.
STRONX, the pultruded composite line of THE FRONT, includes a range of FRP structural shapes designed for industrial frames, roof systems, and support structures. The product range supports applications where durability, consistency, and corrosion resistance are critical.
THE FRONT focuses on stable manufacturing processes and export-oriented supply, enabling FRP structural frames to be delivered for both domestic and international industrial projects.
Long-Term Value of FRP Structural Frames
The long-term value of FRP structural frames lies in reduced lifecycle cost rather than initial material price.
By minimizing corrosion-related maintenance, repainting, and replacement, FRP frames lower operational expenses over time. For facilities operating continuously or in difficult environments, this reliability translates into improved productivity and reduced risk.
As industrial environments become more demanding, structural solutions that prioritize durability and consistency are increasingly favored.
FRP structural frames provide a durable and reliable alternative to traditional materials in corrosive industrial environments.
By combining corrosion resistance, lightweight performance, and predictable structural behavior, FRP frames improve long-term durability in applications such as industrial roof frames, warehouse structures, and support systems.
Through its STRONX product line, THE FRONT supports industrial projects with FRP structural frames designed to withstand aggressive environments while reducing maintenance demands. As industries seek sustainable and resilient structural solutions, FRP structural frames continue to demonstrate clear advantages in corrosive conditions.